CBAC provides networkwide protection by using the following functions:
CBAC is a software-based firewall feature that offers dynamic traffic filtering capabilities to filter TCP and UDP packets based on upper-layer application protocols such as HTTP, SMTP, and FTP to name a few. For CBAC to function, the network must be divided in two logical segments: "trusted or protected" and "untrusted or unprotected." The principal of CBAC traffic filtering is to allow any traffic that originates from the trusted network and goes out to the untrusted network through the firewall.
CBAC inspects traffic that traverses through the firewall and manages state information for all the TCP and UDP sessions. This state information is used to create temporary openings through the firewall to allow return traffic and additional data connections for permissible sessions.
With the application-level awareness, CBAC maintains TCP and UDP connections, which provide all the necessary information to perform deep packet inspection in the data payload for any malicious activity. For example, as shown in Figure 5-1, an intruder could craft a malicious, unauthorized, non-SMTP activity packet encapsulated in an SMTP packet destined on TCP port 25. In conventional access list filtering, this packet would be allowed because it would check only the Layer 3 and Layer 4 information in the packet. With CBAC packet inspection, the packet is further examined for known SMTP operations as per RFC standards, and any noncompliance operation (illegal commands) in the payload is blocked.
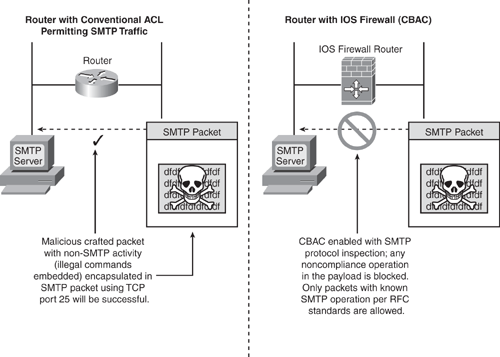
Based on this inspection method, several types of network attacks that use the embedding technique to pass malicious traffic encapsulating in known application protocol packets can be prevented.
In addition to traffic inspection, CBAC can generate real-time event alerts and audit trails for all the session information maintained in the state table. The enhanced audit trail feature uses SYSLOG to track all network transactions, recording information such as source/destination host addresses, ports used, and the total number of transmitted bytes with time stamps. This information can be valuable for advanced session-based reporting, anomaly identification, or the charting of network baselines. For any suspicious activity, CBAC can send real-time event alerts using SYSLOG notification messages to a management console. CBAC inspection rules can be configured for reporting event alerts and audit trail information on a per-application-protocol basis.