After the logical network flow and topology is determined, it is time to configure the switch, the Router/MSFC, and the FWSM. This section describes how to assign VLANs to the FWSM. The FWSM does not include external physical interfaces. Instead, it uses VLAN interfaces. Assigning VLANs to the FWSM is similar to assigning a VLAN to a switch port, in that the FWSM includes an internal interface to the Switch Fabric Module (if present) or the shared bus.
Perform the following basic steps to initialize the FWSM:
Step 1. | Define the VLANs on the switch VLAN database and assign the VLANs to switch ports. |
Step 2. | Assign (push) the VLANs to the FWSM by using the firewall vlan-group command, and assign the firewall group to the FWSM by using the firewall module command. |
Step 3. | Create a Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) on the MSFC. |
Step 4. | On the FWSM, use the nameif command to assign the SVI to the corresponding FWSM interface, and assign an IP address on the FWSM interfaces using the ip address command. |
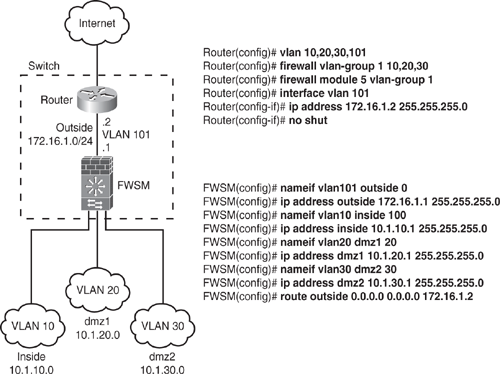
Figure 6-24 shows an example of how to set up a basic firewall configuration with the router on the outside. The example creates four VLANs on the switch (VLAN 10, 20, 30, and 101), assigns the VLANs to the firewall VLAN group 1, and assigns group 1 to the FWSM in slot 5. VLAN 101 is the SVI created on the router, and the IP address 172.16.1.2 is assigned, which will be used as the default gateway on the FWSM. Only one SVI is created on the router for VLAN 101. (Do not configure SVI for VLAN 10, 20, or 30, because it will cause inter-VLAN routing, causing traffic to pass around the FWSM and thereby bypass it.) For this security reason, by default, only one SVI can exist between the router and the FWSM. Continue the configuration on the FWSM side. Corresponding VLANs are mapped with the nameif command, and IP addresses are assigned accordingly.
Note
The examples shown in this chapter are based on Cisco IOS Software output only. Refer to Cisco documentation for CatOS (Hybrid mode).
Use the show firewall vlan-group command to view the group configuration and the show firewall module to view VLAN group numbers for all modules.
After the basic configuration is finished, as shown in Figure 6-24, the FWSM can be managed in a manner that is similar to the PIX firewall. All firewall features such as mode (router or transparent), single or multiple contexts, network address translation, IP routing, failover, and all other firewall functions are more or less similar and are configured in the same way as the PIX firewall, as shown in earlier sections.