The demand for comprehensive network security has never been greater. Malicious users remain a threat; they steal, manipulate, and impede information, and they interrupt network services. Numerous solutions are available to address a network's perimeter defense at the boundaries, but the greatest threat of information theft and unauthorized access remains within the internal network at the access level.
Organizations rely on networks to efficiently and securely manage who and what can access the network, and when, where, and how network access can occur. As threats of network service disruption by unauthorized access become more numerous, network reliability and security become more critical at each layer within the network.
The relative ease of physical and logical access to a network has been extended to enable a greater level of mobility, providing several benefits to business operations and overall productivity. However, this greater level of mobility brings concerns with it and demands more and more security solutions.
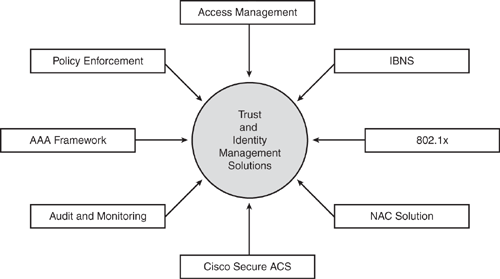
Cisco security portfolio provides an ecosystem of Cisco Trust and Identity Management solutions by offering access control at the media access level (data link Layer 2) through the implementation of the Cisco IBNS (Identity-Based Networking Services) and 802.1x technology.
Note
The data link layer is Layer 2 of the seven-layer OSI model. The data link layer (Layer 2) responds to service requests from the network layer (Layer 3) and issues service requests to the physical layer (Layer 1).
The Layer 2 access control solution provides secure network access and admission at any point in the network, and it isolates and controls unauthorized devices that are attempting to access the network. Layer 2 access control provides security via a user-based policy enforcement model at the port level, media access level, or logical connection.
This chapter outlines a framework and system based on technology standards that provide identity-based network access control, down to the user at the access port level at Layer 2.
The Cisco Trust and Identity Management Solutions offer the following essential security functions:
Enforcement: Authenticates entities and determines access privileges based on policy.
Provisioning: Authorizes and controls network access and pushes access policy enforcement to network devices via VLANs, ACLs, and so on.
Monitoring: Accounting, auditing, and forensic tools allow system administrators to track the who, what, when, where, and how of network activity.
The Cisco Trust and Identity Management solution comprises three technologies:
Secure Identity Management: Provides secure access control and integrity for every network device across the network by applying an access policy that uses the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) framework. Various solutions addressing this domain have been covered in Chapters 8, 9, and 10.
Identity-Based Networking Services (IBNS): A technology solution that expands network access security by using the 802.1x technology. IBNS provides identity-based network access control and policy enforcement at the port level. This chapter covers primarily the IBNS and 802.1x technology solutions.
Network Admission Control (NAC): An integrated set of technologies and solutions built on an industry initiative led by Cisco. NAC provides policy enforcement on all devices seeking network access by allowing network access only to trusted endpoints and to those compliant with network security policies. Examples of those granted access include devices with up-to-date antivirus, OS version, or patch updates, thereby limiting damage from emerging security threats. The NAC solution is able to deny or restrict network access to any noncompliant device as well as quarantine and remediate noncompliant devices. The Cisco NAC solution will be covered in Chapter 13, "Network Admission Control (NAC)."
Building on the three types of technologies of the Cisco Trust and Identity Management solution, this chapter primarily covers how the Cisco IBNS and 802.1x combined technologies provide an important addition to the tools available for securing the network.
Figure 11-1 summarizes the Cisco Trust and Identity Management Solutions.