Table 19-3 shows a basic comparison between L3VPN and L2VPN solutions and describes the type of data each can carry.
Selecting L3VPN over L2VPN depends on how much control the enterprise wants to retain within its network. With L3VPN, the service provider is involved because it performs the routing; whereas with L2VPN, the service provider is not involved, because virtual tunnels and circuits are used instead.
Subscribers have various requirements and can take advantage of L3VPN and L2VPN as needed.
L3VPN is useful to subscribers who prefer to outsource their routing to service providers. The service provider manages routing for the customer's sites.
L2VPN is useful to subscribers who run their own Layer 3 networks over the WAN and require Layer 2 connectivity from service providers. In this case, the subscriber manages its own routing information.
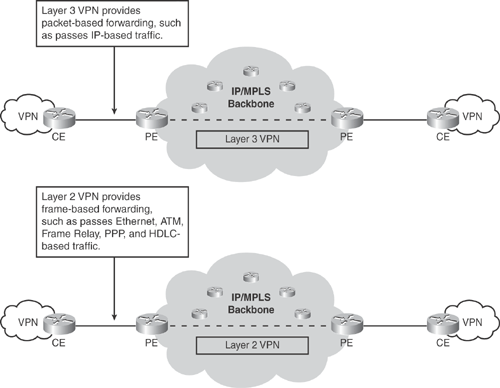
Figure 19-5 illustrates the Layer 3 and Layer 2 VPN data forwarding scenarios over the MPLS core. Both Layer 3 and Layer 2 VPN services are offered from the edge of a network.