Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) over MPLS solution offers frame-based data forwarding for any Layer 2 transport technology.
Cisco IOS Software supports L2VPN architecture by encapsulating any Layer 2 traffic such as Ethernet, Frame Relay, ATM, High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC), and Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) over MPLS or IP network infrastructures.
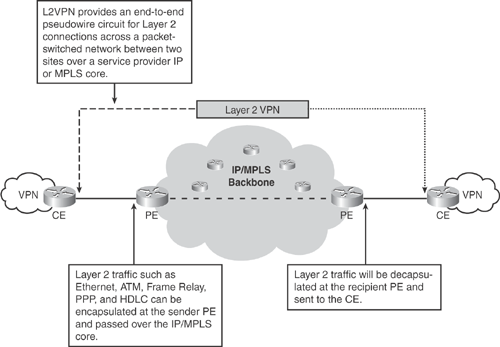
L2VPN architecture provides a point-to-point Pseudowire between the provider edge (PE) routers. Pseudowire emulates a point-to-point Layer 2 connection over Layer 3. The PE router encapsulates any receiving Layer 2 traffic at the sender's edge PE and decapsulated at the recipient's edge PE.
Figure 19-7 illustrates the L2VPN pseudowire end-to-end connection.
Note
L2VPN services are complementary to L3VPN services.
The following two emerging L2VPN service architectures are gaining momentum and generating interest among service providers and enterprises:
Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS): VPWS is a point-to-point technology that enables the transport of Layer 2 services such as Ethernet, Frame Relay, ATM, HDLC, and PPP over a packet-based infrastructure across a service provider IP/MPLS cloud. VPWS can be used to transport existing Layer 2 networks over MPLS- or IP-based networks.
There are two common Cisco pseudowire technologies available: Any-Transport-over MPLS (AToM) for MPLS networks and L2TPv3 (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol version 3) for native IP networks. Both AToM and L2TPv3 support the transport of Ethernet, Frame Relay, ATM, HDLC, and PPP traffic over an IP or MPLS core.
Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS): VPLS is a multipoint L2VPN technology that provides the emulation for Ethernet, connecting multiple sites over a packet-based infrastructure across a service provider IP/MPLS cloud. In essence, VPLS architecture provides multipoint Layer 2 connectivity over Layer 3 network architecture. Services in VPLS solutions appear to be on the same LAN segment regardless of the physical location.
With VPLS, Ethernet LAN can be extended to anywhere across the provider edge network, taking local LAN beyond the physical boundaries. The provider emulates the function of a LAN switch to connect a user LAN to create a single bridge Ethernet LAN.
Note
The main difference between the VPLS and VPWS architecture is that VPLS provides point-to-multipoint service, whereas VPWS provides point-to-point service only.
Table 19-4 compares VPWS and VPLS technologies.
Note
IETF L2VPN is a working group responsible for standardization of Layer 2 VPN architectures, such as VPLS and VPWS. More details can be found at http://www.ietf.org/html.charters/l2vpn-charter.html.