CS-MARS is an appliance-based security information management (SIM) system providing security monitoring and correlation services to identify, contain, and respond to networkwide security threats.
CS-MARS is another key solution that extends the Cisco Self-Defending Network initiative and essential deployment for a security information management system.
CS-MARS offers network intelligence by using sophisticated event correlation technology to precisely identify and correlate events, validate threats, pinpoint attack paths, and provide comprehensive security threat control and mitigation solutions. Through various techniques, CS-MARS maps the entire network, thereby providing complete network visibility and reaction capability by leveraging data from all over the network.
Table 23-1 provides a summary of the common features and capabilities of the CS-MARS appliance-based security information management solution.
| Feature | Capabilities |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Session-Based Correlation |
|
| Topology Discovery | |
| Vulnerability Analysis |
|
| Incident Analysis and Response |
|
| Query and Reporting |
|
| Administration |
|
| The information in Table 23-1 is compiled from Cisco Security Monitoring, Analysis, and Response System 4.3.1 and 5.3.1 at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6241/products_data_sheet0900aecd80272e64.html. | |
CS-MARS is a state-of-the-art security threat mitigation (STM) system providing cutting-edge capabilities. New advanced STM features include data sessionization, topological awareness, and mitigation capabilities.
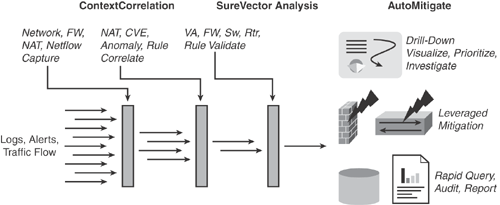
CS-MARS offers security countermeasures by combining state-of-the-art network intelligence, context correlation using the ContextCorrelation feature, vector analysis using the SureVector feature, anomaly detection, hotspot identification, and automated mitigation using the AutoMitigate capabilities. These are defined in the list that follows:
Cisco ContextCorrelation: CS-MARS software includes an integrated ContextCorrelation feature that performs data normalization against the topology by processing the captured raw events and logs, device configurations, and same source and destination applications across Network Address Translation (NAT) boundaries. Corresponding events are grouped into sessions in real-time. System-defined and user-defined correlation rules are then applied to multiple sessions to identify meaningful incidents. CS-MARS has a default set of comprehensive predefined rules, which identify a majority of common anomaly scenarios and day-zero attacks. ContextCorrelation significantly reduces raw event data by packaging the incidents into groups, rather than individual data points.
Cisco SureVector: CS-MARS software includes the integrated SureVector analysis engine that allows the processing of similar event sessions to determine whether threats are valid and have been successful in causing damage. CS-MARS validates threat information by performing endpoint scans to eliminate false positives and by using the SureVector™ engine to investigate the raw data, device logs, and third-party vulnerability assessment data. Further fine-tuning of the system can reduce additional false positives.
Cisco AutoMitigate: CS-MARS software includes an integrated AutoMitigate feature that allows a real-time dynamic mitigation solution to stop the attacks. CS-MARS can identify the offending and compromised system down to the endpoint MAC address. Using the AutoMitigate feature, CS-MARS can identify available devices along the attack path and dynamically provide mitigation recommendations by suggesting the relevant device commands and configurations that can be deployed on a particular device to quickly and accurately prevent or contain an attack.
Figure 23-1 shows CS-MARS with extended security threat mitigation (STM) system capabilities of using Cisco ContextCorrelation, SureVector, and AutoMitigate features.
CS-MARS offers an automated event log collection system capturing data from various heterogeneous network devices (Layer 2 and Layer 3) across multiple devices such as routers, switches, firewalls, IDS, IPS, and server-based systems, aggregating all into a centralized database to perform intelligent correlation and to group related events of the same traffic flow.
Figure 23-2 depicts how CS-MARS works by capturing raw data and configuration from various devices and processing the isolated events, performing analysis, and correlating threat information into valid incidents, thus greatly reducing false positives.
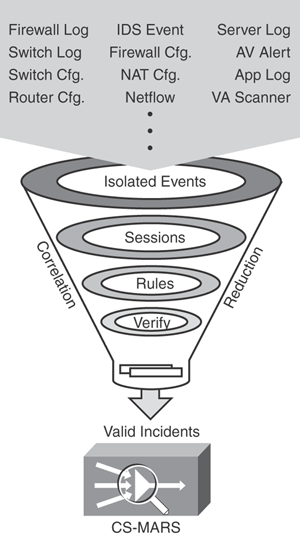
CS-MARS uses a policy-based approach to block security attacks by transforming raw data into actionable intelligence, identifying and correlating real security threats, and providing recommendations for mitigation recommendations.
CS-MARS builds topological awareness and paints network maps of the entire topology by performing discovery of the network devices within the network. CS-MARS is capable of capturing a wide range of Cisco and non-Cisco devices, including Layer 2 and Layer 3 devices.
CS-MARS has an integrated network discovery function that builds a topology map containing device configuration and current security policies, which enables it to model packet flows through a network.
CS-MARS reads a network device configuration and populates into a central database, allowing the construction of a complete topological map of the network.
CS-MARS provides network behavioral analysis by profiling network traffic, capturing raw data, and aggregating and correlating from heterogeneous devices from a wide range of devices in a single CS-MARS appliance.
Figure 23-3 shows CS-MARS capturing raw data and configuration files from various heterogeneous network devices (Layer 2 and Layer 3).
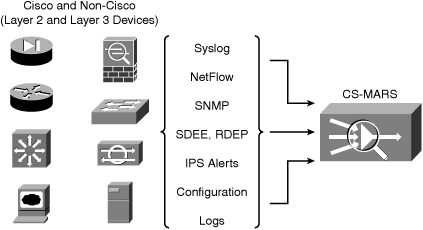
CS-MARS is capable of receiving high volumes of data with its secure and stable architecture. It can receive more than 15,000 events per second or more than 300,000 Cisco NetFlow events per second.
CS-MARS offers a high-performance aggregation and consolidation service by capturing millions of raw events and grouping them efficiently into classified incidents with unprecedented data reduction.
CS-MARS is able to deliver high-performance correlation through inline processing logic and the use of an embedded high-performance database system.
Table 23-2 is a list of supported reporting devices (Cisco and non-Cisco) that can be captured by CS-MARS appliance.
| Device Type | Cisco and Non-Cisco Devices |
|---|---|
| Network | Cisco IOS Software, Cisco Catalyst OS software, Cisco NetFlow, and Extreme Extremeware |
| Firewall/VPN | Cisco ASA Software, Cisco PIX Security Appliance, Cisco IOS Firewall, Cisco Firewall Services Module (FWSM), Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator, Checkpoint Firewall-1 NG and VPN-1 versions, NetScreen Firewall, and Nokia Firewall |
| Intrusion Detection and Prevention | Cisco IDS and IPS Sensor, Cisco IDS Module, Cisco IOS IPS, Cisco ASA IPS Module, Enterasys Dragon NIDS, ISS RealSecure Network Sensor, Snort NIDS, McAfee Intrushield NIDS, NetScreen IDP, OS, and Symantec ManHunt |
| Vulnerability Assessment | eEye REM, Qualys QualysGuard, and FoundStone FoundScan |
| Host Security | Cisco Security Agent (CSA), McAfee Entercept, and ISS RealSecure Host Sensor |
| Host Logs | Windows NT, 2000, and 2003 (agent and agentless), Solaris, and Linux |
| Antivirus | Symantec Antivirus, Cisco Incident Control System (Cisco ICS), Trend Micro Outbreak Prevention Service (OPS), Network Associates VirusScan, and McAfee ePO |
| Authentication Servers | Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) |
| Applications | Web Servers (IIS, iPlanet, and Apache), Oracle audit logs, Network Appliance NetCache, and ISS site protector |
| Universal | Universal device support to aggregate and monitor any application syslog |
| Custom | Support additional and custom devices using the custom log parser feature |
| The information in Table 23-2 is compiled from Cisco Security Monitoring, Analysis, and Response System 4.3.1 and 5.3.1 at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6241/products_data_sheet0900aecd80272e64.html. | |
Note
CS-MARS continues to improve its device support. For a comprehensive, up-to-date list with supported version information, refer to the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6241/products_device_support_tables_list.html.
CS-MARS uses various terms to define contextual analysis and the process of threat investigation. These may vary from the traditional terminologies used for other systems:
Event: Each log event (raw data) received by CS-MARS from any reporting device (such as syslog, SNMP trap, NetFlow, IPS alert, Security Device Event Exchange (SDEE), or Windows log) is referred to as an event in CS-MARS. Retrieved raw messages from the reporting devices are mapped into events.
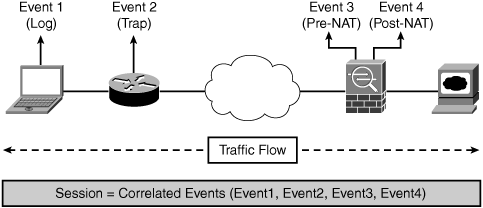
Sessions: Correlated events that are related to the same network flow received from one or more devices. The session is created for like events that are common to a particular criteria—for example, timestamp, source IP address, source port, destination IP address, destination port, or protocol information. Figure 23-4 depicts a CS-MARS session.
Rule: Used to perform logic on events that create sessions and incidents. A rule defines patterns of normalized event types and the notification action CS-MARS will take when the rule fires. These patterns can be signatures of attacks, probes, configuration errors, or anomalous network traffic behavior. CS-MARS has two types of rules: inspection rules and drop rules.
Incident: A session matched against a rule that is indicative of malicious behavior. An incident is triggered when a rule or collection of rules matched. As shown in Figure 23-5, incidents can contain one or more events detailing the event correlation, such as a complete story of an attack. Rules fire to create incidents.
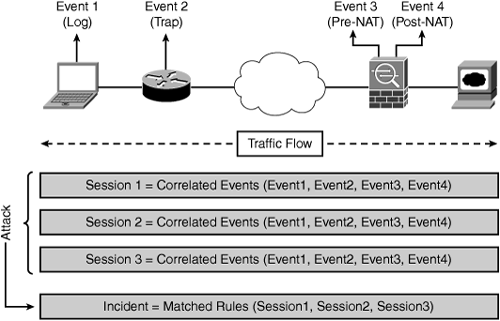
Figure 23-4 depicts how a session is interpreted in CS-MARS.
Figure 23-5 depicts how an incident is interpreted in CS-MARS.
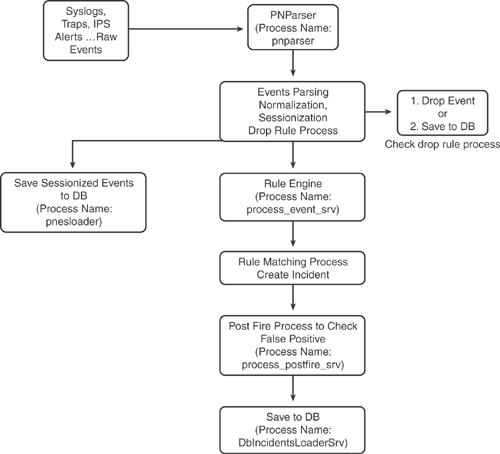
CS-MARS uses the following steps to process events when it receives a raw message.
1. | Receive raw messages from network devices either via pulling mode or listening mode |
2. | Parse raw messages |
3. | Normalize raw messages to events—statically map raw messages from different vendor devices to CS-MARS known event types |
4. | Sessionization/NAT correlation—identify commonality within the event, such as source IP/port, destination IP/port, protocol to sessionize events |
5. | Run events against rule engine |
6. | False positive analysis |
7. | Vulnerability assessment against suspected hosts |
8. | Traffic profiling and statistical anomaly detection |
Figure 23-6 shows the event process flowchart in CS-MARS.
The information in Figure 23-6 is compiled from the Cisco Networkers Breakout Session presentation #BRKSEC-3006—Network Security Monitoring and Correlation with CS-MARS.
CS-MARS interprets false positives differently than other systems. In general terms, when a message is considered a false positive, this means that a system has incorrectly identified an attack but in reality it did not happen. However, in CS-MARS a false positive means the attack was identified correctly but it was unsuccessful against the target victim.
There are four basic types of false positives in CS-MARS:
System Confirmed False Positive
Unconfirmed False Positive
User Confirmed False Positive
User Confirmed Positive
Figure 23-7 illustrates the false positive process flowchart in CS-MARS.
The information in Figure 23-7 is compiled from the Cisco Networkers Breakout Session presentation #BRKSEC-3006—Network Security Monitoring and Correlation with CS-MARS.
