Cisco Security Manager is a market-leading security and policy management software application for managing network security functions.
Cisco Security Manager is an essential tool to centrally provision all aspects of device configuration and security policies for firewalls, including PIX Security Appliance, Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), and Firewall Services Module (FWSM), Virtual Private Networks (VPN) technologies, and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) services across Cisco routers, security appliances, Catalyst 6500/7600 series devices, and Catalyst switch security services modules (VPNSM, FWSM).
Cisco Security Manager offers configuration, deployment, and management services across all major Cisco security devices. Cisco Security Manager can provision small networks of fewer than ten devices and scale to large-scale networks with thousands of devices.
Note
The Cisco Security Manager is part of the Cisco Security Management suite—a framework of products and technologies, delivering scalable policy administration and enforcement for the Cisco Self-Defending Network. The suite also includes the CS-MARS product for monitoring and mitigation. CS-MARS is covered in Chapter 23, "Security Monitoring and Correlation."
For more details about the Cisco Security Management suite, refer to the following Cisco documentation URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns647/networking_solutions_sub_solution_home.html.
Cisco Security Manager provides the capability to deploy and manage security policies on Cisco security devices.
Cisco Security Manager supports integrated provisioning of firewall, VPN, and IPS services across Cisco IOS routers, PIX, and ASA security appliances, and Catalyst 6500/7600 services modules (FWSM and VPNSM).
Cisco Security Manager also supports provisioning of various platform-specific configurations—for example, Interface parameters, Routing protocols, Quality of Service (QoS), Network Address Translation (NAT), Syslog, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Multicast, Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA), and so forth.
Cisco Security Manager offers various features and functions. The following are some of its common capabilities:
A single, integrated application for managing security across all major Cisco security devices
Integrated service-based and device-based provisioning firewall, VPN, and IPS management, all natively from a single interface
Device configuration rollback; capability to roll back to a previous configuration if necessary
Workflow mode
Multiple views for task optimization
Scaling to many hundreds of remote sites
Enforcement of corporate rules and best-practice guidelines
Sophisticated rule analysis and optimization
Collaboration between provisioning, configuration, monitoring, mitigation, and identity
Integration between Cisco Security Manager and CS-MARS
Native IPS Policy Management on IPS, Catalyst, ASA, and ISR platforms
Advanced IOS Interface, platform settings discovery
Transparent device manager read-only cross-launch to access Adaptive Security Device Manager (ADSM), Security Device Manager (SDM), and IPS Device Manager (IDM)
Native IPS management in v3.1 with the same look and feel as other components, such as firewall and VPN management
Capability to discover Cisco IOS Software-based router configurations
Unified Management for FW/VPN/IPS security policies
Complete VPN solution (IPsec, GRE, DMVPN, Site-to-Site, Remote Access, EasyVPN, and SSL VPN)
VPN Discovery support—capability to discover Site-to-Site and Remote-Access VPNs
SSL VPN support on both ASA and IOS platforms
Native Cat6500/7600 support—router ACLs (RACL), VLAN ACLs (VACL), virtual local area networks (VLAN), and the capability to arrange them to the right FWSM and virtual context.
Inventory report showing the managed devices with device status, OS versions, platform, and policies assigned to a particular device
Management protocol connectivity test
Detailed user-activity report showing exactly what the user changed during login
Role-based access control (RBAC) and privilege-based management access integrated with Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) for multiadministrator operations.
High availability
Scaleable deployment through the use of distributed deployment
Automated network and security compliance audit and analysis
Cisco Security Manager provides centralized policy administration of Cisco security appliances, integrated security routers, and security service modules for
Figure 24-1 depicts a high-level overview of Cisco Security Manager providing integrated security management provisioning functions.
The information in Figure 24-1 is taken from the Cisco general product presentation on Cisco Security Manager.
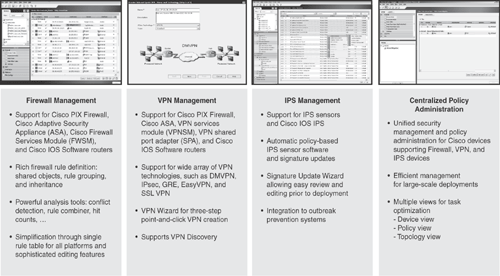
Cisco Security Manager supports configuration and management of Cisco firewall policies across multiple platforms, including
Cisco IOS Software Router
Cisco PIX appliance
Cisco ASA appliance
Cisco Catalyst Firewall Service Modules (FWSM)
Cisco Catalyst 6500/7600
Following are some of the common features and capabilities in the firewall management system:
Unified firewall service/table for all security platforms
Native Cisco IOS Software ACL (non-CBAC) support; permit/deny traffic on interfaces through the use of access control lists (ACL)
Inspection rules; filter TCP and UDP packets based on application-layer protocol session information
AAA and Authentication Proxy rules; filter traffic based on authentication and authorization for users logged in to the network or that access the Internet through HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, or Telnet sessions
Web-filtering rules, using URL-filtering software, such as Websense, to deny access to specific websites
Transparent firewall rules, and enabling transparent firewall device to be deployed in an existing network without having to reconfigure statically defined devices
Reusable shared objects (for example, hosts, networks, services)
Cross-launch of read-only Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) for device status and real-time Syslog, plus the collaboration between Cisco ASDM and Cisco Security Manager
Interface roles (apply rule to group of interfaces)
Intelligent analysis and query of firewall policies
Autogeneration of rules that are required by user policies
Built-in end-to-end VLAN management for Cisco Catalyst 6500 for FWSM configurations
Firewall security context management for Cisco FWSM and Cisco ASA
Discovery and import of external configuration changes
The Cisco Security Manager supports configuration and management of Cisco VPN policies across multiple platforms, including
Cisco IOS Software Router
Cisco PIX Appliance
Cisco ASA Appliance
Cisco Catalyst VPN Service Modules (VPNSM)
Cisco VPN Shared Port Adapter (SPA)
The VPN management system allows setup and configuration of IPsec Site-to-Site and Remote Access VPNs. Supported VPN technologies include
IPsec
GRE
DMVPN
Easy VPN
SSL VPN
Some of the common features and capabilities in the VPN management system are
Support for Site-to-Site and Remote Access VPNs
Easy-to-use three-step wizard-based approach to create an IPsec VPN tunnel
SSL VPN wizard
Support of hub-and-spoke, full-mesh, and point-to-point topologies
Capability to modify Internet Key Exchange (IKE) proposals, Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) settings, Network Address Translation (NAT) traversal, and fragmentation settings
Visualization of VPNs on the topology-centric map
VPN Discovery feature, import existing VPN settings
Virtual routing and forwarding VRF-aware IPsec VPN
IPsec VPN high availability
Cisco Security Manager supports configuration and management of Cisco IPS policies across multiple platforms, including
Cisco IPS 4200 series appliance
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Intrusion Detection System Module (IDSM-2)
Cisco IPS Advanced Integration Module (IPS-AIM) for router
Cisco Advanced Inspection and Protection Security Services Module (AIP-SSM) for ASA
The IPS management system allows setup and configuration of IPS sensor management, including
Automatic policy-based IPS sensor software and signature updates
Signature update wizard allowing easy review and editing prior to deployment
The IPS management system allows setup and configuration of IPS sensors software. Supported IPS Software versions include
Cisco IPS Version 5.1 and 6.0
Cisco IOS IPS 12.4(11)T2 and later
Some of the common features and capabilities in the IPS management system include
Native IPS support with full IPS management integration into Cisco Security Manager.
IPS device-centric signature view.
Policy-centric signature view.
Easy to use three-step wizard-based approach to apply signature update or sensor software update to set devices.
Signature update automation: automatic policy-based IPS sensor software and signature updates.
IPS subscription licensing provisioning.
Enterprise-class operations environment: role-based access control, policy rollback, configuration archive, deployment manager, cloning and creation of signatures, policy sharing, and inheritance.
Cross-launch of embedded IEV (Cisco IPS Event Viewer) to view real-time IPS events and collaborate between security events and policy management.
Cross-launch of Cisco IEV to IPS Rule in Cisco Security Manager. Right-click IPS alert in the IEV event viewer. Click Go to CSM to bring up Cisco Security Manager with the corresponding device and IPS signature selected.
In addition to firewall, VPN, and IPS management, the Cisco Security Manager supports configuration and management of platform-specific configuration parameters, for example:
Interface parameters and settings
Logging setup, server setup, and syslog servers
Multicast
Network Address Translation (NAT), address pools, translation options, and translation rules
IP Routing; Static, Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Open Short Path First (OSPF), Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Service policy rules (priority queues and Quality of Service (QoS)
IOS Security settings, antispoofing, Floodguard, fragment, and timeouts
Manage VLANs, interfaces, and VACLs on Cisco Catalyst 6500 series
The Cisco Security Manager supports the wide range of platform settings in the previous list that supplies coverage beyond the basic firewall, VPN, and IPS services.
Cisco Security Manager is built with robust architecture to centrally provision all aspects of device configuration and security policies for Cisco security devices.
Figure 24-2 illustrates the system architecture of the Cisco Security Manager.
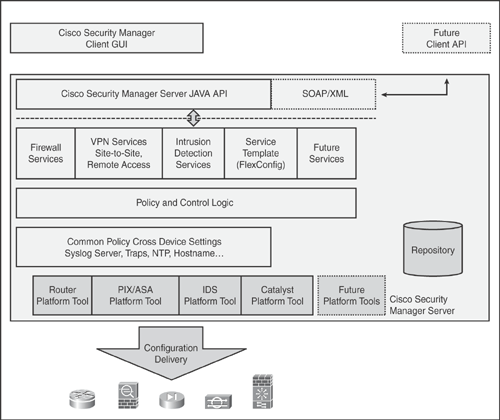
Note
The information in Figure 24-2 is taken from the Cisco general product presentation on Cisco Security Manager.
Cisco Security Manager provides a powerful, user-friendly, easy-to-use interface. The simple and flexible user interface provides users with the capability to perform complex tasks with great ease.
Cisco Security Manager provides three feature-rich, simple-to-use views into the management system for users to manage devices and policies. Users can swap among these user views according to their needs at any time:
Device-centric view (DCV): Enables users to view the properties of devices being managed, add/delete devices from the Cisco Security Manager inventory, and centrally manage all device policies, properties, interfaces, and other related device parameters. As shown in Figure 24-3, the DCV displays on a single screen all devices that are being managed. Specific devices can be selected to view their properties and define their settings and policies. DCV also allows you to define security policies locally on specific devices and further share these policies globally, making them available for assignment to other devices. DCV can be selected by clicking the Device View button from the main page. Figure 24-3 illustrates sample screen capture of a DCV from the Cisco Security Manager.

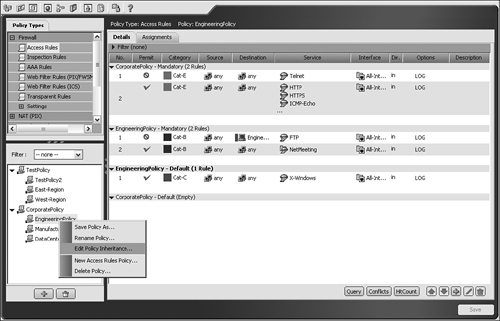
Policy-Centric View (PCV): Enables users to create and manage shared reusable policies at the system level that can be shared among multiple devices for later assignments. With PCV, users can view all the shared policies that are defined for a particular policy type, and create, view, and edit policies and modify their device assignments. Figure 24-4 is a sample screen capture of a PCV from the Cisco Security Manager.
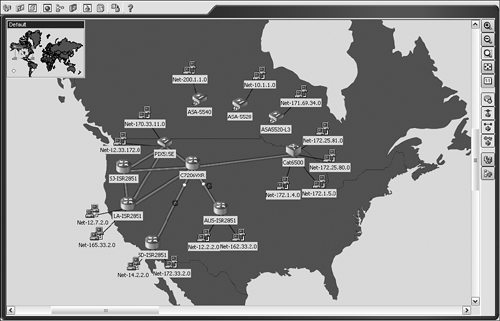
Map View or Topology-Centric View (TCV): Enables users to create customized topology-based visual maps of the network, allowing users to manage the policies directly from the topology view. Within TCV, users can view network connections between devices, link topologies, and configure VPN and access control settings directly from the view maps. TCV provides a graphical view of the VPN and Layer 3 network topology. Figure 24-5 is a sample screen capture of a TCV from the Cisco Security Manager.
Before Cisco Security Manager can manage a device, each device must be configured to communicate with Cisco Security Manager on the required transport protocol and the necessary settings. For example, Cisco Security Manager uses Secure Socket Layer (SSL) as the default transport protocol to communicate with PIX Firewall, Adaptive Security Appliances (ASA), Firewall Service Modules (FWSM), and Cisco IOS routers. Therefore, configure SSL settings on these devices to communicate with Cisco Security Manager before adding them to the device list.
After the device is configured and ready to be managed, add the device to the Cisco Security Manager device inventory from the Device page.
Table 24-1 summarizes the types of devices and the transport protocols used for each device to communicate with Cisco Security Manager.
By default, Cisco Security Manager operates in the nonworkflow mode, which is the simplest approach; that is, select a device, make a change, and deploy the policy.
For more sophisticated and complex policy deployments, Cisco Security Manager provides a structured process for change management that complements the operational environment. For example, there can be different stages in the life cycle of a policy deployment:
Policy definition
Policy approval
Deployment approval
Actual deployment
The Cisco Security Manager workflow mode provides the capability for multiple users to be involved in the entire process.
As illustrated in Figure 24-6, the Security Operations (SecOps) officer can define the policy changes and submit them for approval to a senior authorized officer. After approval, the Network Operations (NetOps) team can generate deployment jobs, which can be approved by a senior authorized officer for deployment.
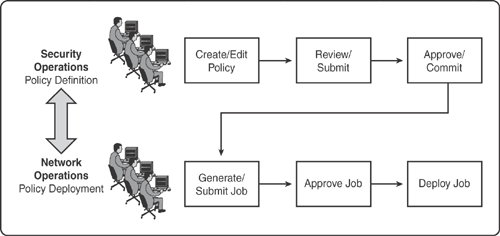
The main advantage of the workflow capability is to allow a separation of responsibilities between those who define the security policies and those who implement them.
Figure 24-6 illustrates a sample structured process for change management from defining to deploying the policy and demonstrating the collaboration across the SecOps and NetOps teams.
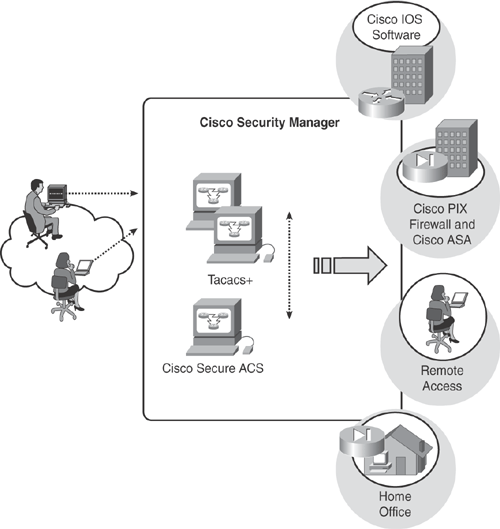
Cisco Security Manager provides two levels of role-based access control providing appropriate separation of ownership and controls to manage the system:
Cisco Security Manager provides a built-in authentication mechanism to verify users and provide them with appropriate access to the management system. The user role dictates the level of permissions (also called privileges), which determine the actions that users with particular roles can perform within Cisco Security Manager. Roles are sets of tasks or operations that are authorized to be performed on a per-user basis. If the user is not authorized for certain tasks or devices, the related menu items, TOC items, and buttons are hidden or disabled. In addition, a message informs users of insufficient privilege when they view the selected item or perform a selected operation.
Cisco Security Manager can also be integrated with Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) for more granular role-based access control, and for a span of control of which devices can be viewed and managed. The integration can also determine which Cisco Security Manager functions can be exercised on those devices and related management functions. Cisco Secure ACS allows for modification of the permissions associated with each Cisco Security Manager role. Users can also be customized by creating specialized user roles with permissions that are targeted to particular tasks. Cisco Secure ACS uses TACACS+ to communicate with the Cisco Security Manager application.
Figure 24-7 illustrates the two role-based access control mechanisms used by the Cisco Security Manager.
The information in Figure 24-7 is taken from the Cisco general product presentation on Cisco Security Manager.
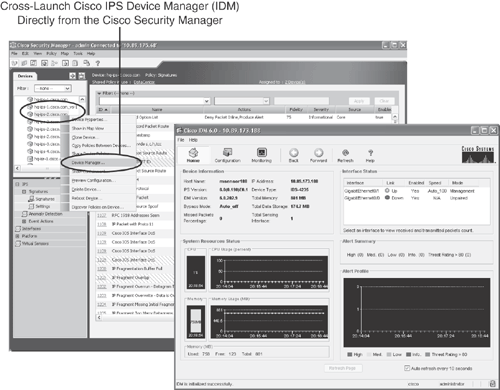
The Cisco Security Manager provides another unique feature—cross-launching, which supplies the capability to open connections to other device manager applications directly from the Cisco Security Manager interface.
Supported cross-launch xDMs include Cisco ASDM, Router and Security Device Manager (SDM), IPS Device Manager (IDM), and IPS Event Viewer (IEV).
This provides great flexibility and faster startup to connect to the device without having a connection from a user desktop. It also provides collaboration between security events and policy management.
Figure 24-8 illustrates an example of opening Cisco ASDM directly from the Cisco Security Manager by right-clicking the managed ASA device and selecting Device Manager to launch the Cisco ASDM application.

Figure 24-9 illustrates another example of opening Cisco IDM (IPS Device Manager) directly from the Cisco Security Manager by right-clicking the managed IPS device and selecting Device Manager to launch the Cisco IDM application.
Similarly, users can cross-launch Cisco Security Manager from the d71471evice manager (xDM) and vice versa.
For example, users can cross-launch Cisco Security Manager from the Cisco ASDM application, as illustrated in Figure 24-10.

From the Cisco ASDM, select the Monitoring tab, select Logging, go to Log Buffer, and click View, and the log buffer screen panel will show all the log outputs captured from Cisco ASA.
Then, right-click any particular log entry and select Goto Rule in CSM to cross-launch Cisco Security Manager and review the corresponding Access Rule policy that triggered this log.
This feature gives enhanced power to the user to manage and correlate entries between applications without having to connect to the device directly. All this can be managed through single-click options.
Figure 24-10 shows a sample log entry output in Cisco ASDM logs. Right-click the log entry to launch the Cisco Security Manager and view the corresponding access rule that triggered the log.
Furthermore, a packet tracer option is available in Cisco ASDM to gain more insight into the packet flow, route flow, and relevant filters pertaining to the log entries.
Cisco Security Manager provides configuration and management services across multiple Cisco platforms and OS versions.
Table 24-2 provides a complete list of devices with OS versions supported by Cisco Security Manager.
Cisco Security Manager can be installed on a Windows-based server that is using either one CPU or multiple CPUs.
Table 24-3 describes the minimum server requirements for installing Cisco Security Manager and highlights the restrictions.
| Component | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| System Hardware | |
| File system | NTFS |
| Memory (RAM) | 2 GB |
| System Software | One of the following:
Note: Cisco Security Manager supports only U.S. English and Japanese versions of Windows. Microsoft ODBC Driver Manager 3.510 or later is also required so that your server can work with Sybase database files. |
| Browser | One of the following:
|
| Compression Software | WinZip 9.0 or compatible |
| Hard Drive Space | 20 GB |
| IP Address | One static IP address. If the server has more than one IP address, disable all but one address. The Cisco Security Manager installer displays a warning if it detects any dynamic IP addresses on the target server. Dynamic addresses are not supported. |
| The information in Table 24-3 is taken from "Cisco Security Manager 3.1 Data Sheet" at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6498/products_data_sheet0900aecd8062bf6e.html. | |
Table 24-4 describes the minimum client requirements for installing Cisco Security Manager and highlights the restrictions.
| Component | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| System Hardware |
|
| Memory (RAM) | 1 GB |
| Virtual Memory/Swap Space | 512 MB |
| Hard Drive Space | 10 GB |
| Operating System | One of the following:
|
| Browser | One of the following:
|
| Java | The Cisco Security Manager Client includes an embedded and completely isolated version of Java. This Java version does not interfere with your browser settings or with other Java-based applications. If you try to open Cisco Security Manager but do not have the required version of Java, your Cisco Security Manager server will display a message that tells you how to download and install the required Java version. |
| The information in Table 24-4 is taken from "Cisco Security Manager 3.1 Data Sheet" at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6498/products_data_sheet0900aecd8062bf6e.html. | |
Required traffic flows identify the necessary protocol and port numbers that must be allowed by firewalls/ACLs if they separate the Cisco Security Manager from a supporting device (as listed in Table 24-2). Several protocol and port numbers are used for varying functions when the Cisco Security Manager communicates with a device. Various Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ports need to be enabled for use by the Cisco Security Manager and its associated applications on the server to support their associated services.
Table 24-5 identifies the various traffic flows and the associated protocol and port numbers required to be opened if a gateway, firewall, ACL, or any type of filtering device exists between Cisco Security Manager and the service/device.
| Service | Used For/Used By | Port | Protocol | Inbound | Outbound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ping | Resource Manager Essentials (RME) | — | ICMP | — | X |
| SSH | Common Services | 22 | TCP | — | X |
| RME | 22 | TCP | — | X | |
| Telnet | Common Services | 23 | TCP | — | X |
| DM 6500/7600 | 23 | TCP | — | X | |
| RME | 23 | TCP | — | X | |
| TACACS+ (for ACS) | Common Services | 49 | TCP | — | X |
| RME | TCP | — | X | ||
| Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) | Common Services | 69 | UDP | X | X |
| HTTP | Common Services | 80 | TCP | — | X |
| DM 6500/7600 | TCP | — | X | ||
| SNMP (polling) | Common Services | 161 | UDP | — | X |
| SNMP (traps) | Common Services | 162 | UDP | — | X |
| HTTPs (SSL) | Common Services | 443 | TCP | X | — |
| Security Manager | 443 | TCP | — | X | |
| AUS | 443 | TCP | X | — | |
| Syslog | Common Services | 514 | UDP | X | — |
| Remote Copy Protocol | Common Services | 514 | TCP | X | X |
| VisiBroker IIOP port for gatekeeper | Common Services | 1683/1684 | TCP | X | X |
| HTTP | Common Services | 1741 | TCP | X | — |
| Security Manager | 1741 | TCP | X | — | |
| MySQL | Security Manager | 3306, 5501 | MySQL | X | X |
| Cisco IPS Event Viewer | Security Manager server | 60002, 60003 | TCP | X | X |
| Security Manager client | 5001 | TCP | X | X | |
| HIPO port for CiscoWorks gatekeeper | Common Services | 8088 | TCP | X | X |
| Tomcat shutdown | Common Services | 9007 | TCP | X | — |
| Tomcat Ajp13 connector | Common Services | 9009 | TCP | X | — |
| Database | Security Manager | 10033 | TCP | X | — |
| License Server | Common Services | 40401 | TCP | X | — |
| Daemon Manager | Common Services | 42340 | TCP | X | X |
| Osagent | Common Services | 42342 | UDP | X | X |
| Database | Common Services | 43441 | TCP | X | — |
| DCR and OGS | Common Services | 40050–40070 | TCP | X | — |
| Event Services | Software Service | 42350/44350 | UDP | X | X |
| Software Listening | 42351/44351 | TCP | X | X | |
| Software HTTP | 42352/44352 | TCP | X | X | |
| Software Routing | 42353/44353 | TCP | X | X | |
| Transport Mechanism (CSTM) | Common Services | 50000–50020 | TCP | X | — |
| The information in Table 24-5 is taken from "Installation Guide for Cisco Security Manager 3.1—Requirements and Dependencies" at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/security_management/cisco_security_manager/security_manager/3.1/installation/guide/requirem.html. | |||||
Several other features are unique to Cisco Security Manager and can be used as required.
For more details to install and configure Cisco Security Manager, refer to the following Cisco documentations:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6498/prod_installation_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6498/products_user_guide_list.html