Cisco Router and Security Device Manager (SDM) is a secure web-based device-management tool integrated in the Cisco IOS Software to manage Cisco routers.
Cisco SDM greatly improves productivity, simplifies router and security configuration through step-by-step smart wizards, offers proactive management through performance monitoring, and helps troubleshoot complex network and VPN connectivity issues.
The main advantage of using Cisco SDM is for the non-expert users who are not very familiar with Cisco IOS Software and its features, because it provides an easy-to-use graphical management system to aid in day-to-day operations. For the more experienced users who are familiar with Cisco IOS Software, the Cisco SDM offers advanced configuration tools to quickly configure and fine-tune their work. Users can review the commands generated by the Cisco SDM before pushing the final configuration changes to the router.
Cisco SDM can be used for day-to-day operations such as configuration tuning, monitoring, fault management, and troubleshooting.
Cisco SDM provides an easy-to-use browser-based interface for deploying and monitoring Cisco routers without requiring advanced knowledge of the command-line interface (CLI). With Cisco SDM, users can remotely manage and configure dynamic routing, LAN, WAN, WLAN, interfaces, NAT, firewall, VPN, IPS, QoS, and various other basic and advanced IOS router and security features.
Cisco SDM offers various features and functions. The following are some of its common capabilities for configuring and deploying Cisco Routers using a web-based management interface:
Web-based management application integrated into Cisco IOS Software.
Secure remote management to Cisco Router using SSL and SSHv2 connections.
Router security audit for assessing vulnerabilities and providing recommendations for best practices.
One-step router lockdown feature to enable or disable Security and IOS configurations without requiring security expertise or knowledge of Cisco IOS Software configuration.
Smart Wizards for frequent router and security configuration tasks.
Capability of configuring basic to advanced level router configuration parameters.
Support for policy-based firewall and ACL management.
Support for IOS-based IPS.
Cisco Easy VPN Server configuration and real-time monitoring of remote access VPN connections.
Support of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), leveraging the Cisco IOS Software CLI role-based access feature by providing four factory default access profiles: Administrator, Firewall-Admin, Monitor, and EasyVPN Remote.
Real-time bandwidth and resource monitoring and traffic performance using NBAR and QoS policies.
Provisioning of digital certificates using the Cisco IOS CA server feature.
Customized task-based wizards and an easy-to-use GUI interface to configure common router and security features such as IP Routing, Interface parameters, NAT, QoS, ACL, AAA, VPN, firewall, and IPS.
NAC support.
Granular protocol inspection.
Threat control and intrusion prevention.
Dynamic DNS support to run services without a dedicated static IP address. Supported service providers include www.justlinux.com, www.zoneedit.com, dup.hn.org, members.dyndns.org, www.dyns.cx, cgi.tzo.com, and members.easydns.com.
Easy-to-configure wizards for VPN deployments.
Low overhead with negligible performance impact on router dynamic random access memory (DRAM) or CPU.
Cisco Security Device Manager (SDM) user interface and online help is available in six languages, translated into Japanese, Simplified Chinese, French, German, Spanish, and Italian.
Cisco SDM is an integrated solution embedded within the Cisco IOS Software release. Cisco SDM communicates with routers for two purposes:
Connects to the router to access the Cisco SDM application files for download to the local desktop PC. Cisco SDM uses HTTP/HTTPS to download the application files (sdm.tar and home.tar) to the local desktop PC.
Connects to the router to read and write the router configuration and real-time status monitoring. Cisco SDM uses a combination of HTTP/HTTPS and Telnet/SSH to read and write the router configuration.
Cisco SDM can be launched remotely from any user desktop PC using HTTP, HTTPS, SSL, Telnet, and SSH Protocol connections. The SSL and SSH technology provides a secure connection to manage Cisco IOS Software routers remotely over the Internet or any shared network without compromising the integrity.
The preferred communication protocol used by Cisco SDM is HTTPS (using browser-based SSL) to connect to the router for secure remote management. Users can choose to use non-SSL, less secure standard HTTP-based browsing, too, but it is not recommended.
Users can launch Cisco SDM from a supported Internet browser using the router IP address as follows (HTTP or HTTPS):
https://router_ip_address
Figure 24-11 illustrates a user establishing a secure connection to launch Cisco SDM over the Internet using browser-based SSL technology.
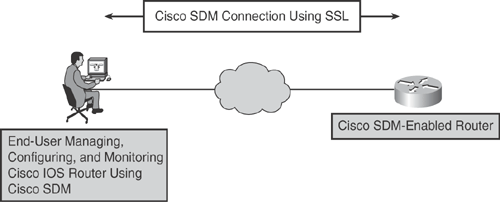
Figure 24-12 shows the Cisco SDM home page when the application is launched.
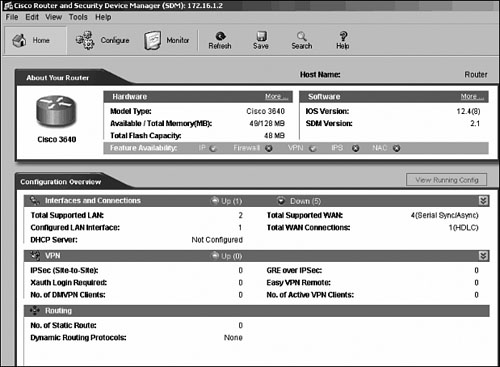
The Cisco SDM home page provides comprehensive information regarding the device, including the following:
Hardware model of the router
Cisco IOS Software version
Available and total memory on the router
Flash memory
Features available in the IOS loaded on the router
Totally supported and configured LAN interfaces
Totally supported WAN connections
IP routing status (static, RIP, OSPF, EIGRP)
VPN deployments (Generic Routing Encapsulation [GRE], IP Security [IPsec], dynamic multipoint VPN [DMVPN], Easy VPN)
Configuration summary
The green circles show the features supported on the router, and the red circles show the features that are not supported.
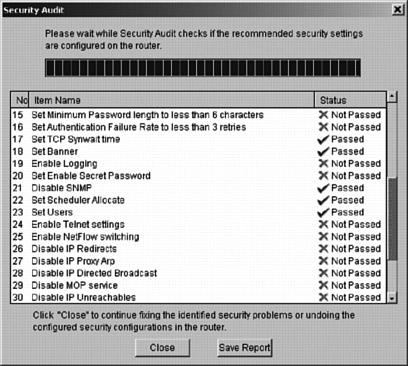
Cisco SDM provides an intuitive router security audit feature with one-step security audit capability that validates router configurations against a list of common security vulnerabilities and Cisco recommended settings, and provides a summary of recommended best practices.
The audit report highlights the potential security problems identified in the router configuration and can generate corresponding configurations to correct the shortfalls.
Figure 24-13 shows a sample screen capture from the Router Security Audit report.
In addition to the Router Security Audit function, Cisco SDM can perform a one-step router-lockdown function to configure the router for recommended best practices security configuration.
Table 24-6 lists features that are enabled or disabled when using the one-step lockdown feature.
| One-Step Lock-Down Action Items | Cisco IOS Software Equivalent |
|---|---|
| Disable Finger Service | no service finger |
| Disable Packet Assembler/Disassembler (PAD) | no service pad |
| Disable Small Servers (TCP and User Datagram Protocol [UDP]) | no service tcp-small-servers no service udp-small-servers |
| Disable BOOTP | no ip bootp server |
| Disable Identification Service | no ip identd |
| Disable Cisco Discovery Protocol | no cdp run |
| Disable Source Routing | no ip source-route |
| Enable Password Encryption | service password-encryption |
| Enable TCP Keepalives for Inbound and Outbound Telnet Sessions | service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out |
| Sequence Number and Time Stamps of All Debug and Log Messages | service timestamps debug datetime localtime show-timezone msec
service timestamps log datetime localtime show-timeout msec service sequence-numbers |
| Enable Cisco Express Forwarding or Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding | ip cef |
| Cisco IOS Software Autosecure Residues | no ip gratuitous-arps |
| Minimum Password Length | security passwords min-length 6 |
| Lock Access to Console or vty Line After Unsuccessful Attempts | security authentication failure rate 3 log |
| Tune Scheduler Interval or Allocation | scheduler interval 500 scheduler allocate 4000 1000 |
| Set tcp synwait Time to 10 Seconds | ip tcp synwait-time 10 |
| Text Banner | Banner—"Authorized access only. Disconnect IMMEDIATELY if you are not an authorized user!" |
| Enable Logging for Security and Sequence Numbers with Input for Logging Server | logging on
logging console critical logging trap debugging logging buffered 51200 |
| For Cryptographic Cisco IOS Software Images, Enable Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol and Serial Control Protocol (SCP) for Access and File Transfer Set SSH Timeouts and Retries to the Minimum Possible | ip ssh time-out 60
ip ssh authentication-retries 2 ! line vty 0 4 transport input ssh telnet ! |
| Disable SNMP if Not Being Used | Only Disable SNMP: no snmp-server |
| Enable NetFlow on Software Forwarding Platforms | interface <all-interfaces> ip route-cache flow |
| Disable Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Redirects | interface <all-interfaces> no ip redirects |
| Disable Proxy-arp | interface <all-interfaces> no ip proxy-arp |
| Disable Directed Broadcast | interface <all-interfaces> no ip directed-broadcast |
| Disable Maintenance Operation Protocol (MOP) Service on Ethernet Interfaces | interface <all-Ethernet-&-FastEthernet-interfaces> no mop enabled |
| Disable ICMP Unreachables on All Interfaces | interface <all-interfaces> no ip unreachables |
| Disable Mask Reply Messages | interface <all-interfaces> no ip mask-reply |
| Disable Sending Unreachable Messages to the Source for the Packets That Are Discarded or Routed to NULL | interface null 0 no ip unreachables |
| The information in Table 24-6 is taken from "Cisco Router and Security Device Manager Q&A" at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/products_qanda_item0900aecd800fd11b.shtml. | |
Cisco SDM provides an intuitive monitor mode for router health checks. Monitor mode can provide a graphical status displaying important information related to the router's resource performance. For example, the following information can be displayed: whether the interface status is up or down, the CPU usage, and memory usage accordingly.
Using the integrated routing and security features, Cisco SDM provides in-depth diagnostics and troubleshooting of WAN and VPN connections.
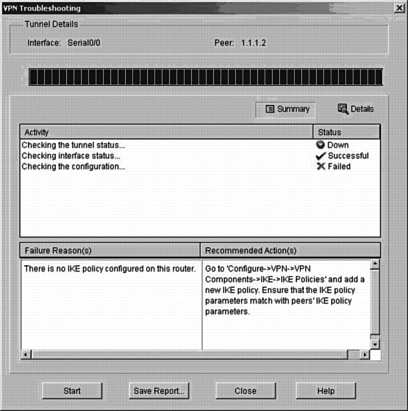
Figure 24-14 shows an example of VPN troubleshooting. Cisco SDM verifies multiple items to troubleshoot the failed VPN connection, identify the fault, and provide recommendations to correct the issue. Some of the basic tasks performed include checking the interface status, IP connectivity, and complete VPN configuration from ISKAMP settings to Crypto Map parameters. At each stage, Cisco SDM provides status information for each test function performed, so that the user can easily understand and determine the root cause. Finally, Cisco SDM will provide possible reasons of failure and provide Cisco TAC recommended actions to be taken for recovery. As shown in Figure 24-14, Cisco SDM performed several checks to verify the VPN failure, has identified an IKE policy configuration issue, and recommends configuring the relevant IKE proposals on the router.
Cisco SDM is supported on all major Cisco routers. Table 24-7 shows a list of Cisco routers and Cisco IOS Software versions supported by the Cisco SDM application.
| Router | Cisco IOS Software Version |
|---|---|
| Cisco Small Business 101, 106, and 107 | 12.3(8)YG or later |
| Cisco 831 and 837 | 12.2(13)ZH or later 12.3(2)T or later |
| Cisco 836 | 12.2(13)ZH or later
12.3(2)XA or later 12.3(4)T or later |
| Cisco 851, 856, 871, 876, 877, and 878 | 12.3(8)YI or later |
| Cisco 1701, 1710, 1711, 1712, 1721, 1751, 1751-V, 1760, and 1870V | 12.2(13)ZH or later
12.3(13)T3 or later 12.3(1)M or later |
| Cisco 1801, 1802, 1803, 1811, and 1812 | 12.3(8)YI or later |
| Cisco 1841 | 12.3(8)T4 |
| Cisco 2610XM, 2611XM, 2620XM, 2621XM, 2650XM, and 2651XM Multiservice Routers, and Cisco 2691 Multiservice Routers | 12.2(15)ZJ3 or later
12.2(11)T6 or later 12.3(1)M or later |
| Cisco 2801, 2811, 2821, and 2851 | 12.3(8)T4 or later |
| Cisco 3620, 3640, 3661, and 3662 | 12.2(15)ZJ3 or later
12.211)T6 or later 12.3(1)M or later |
| Cisco 3725 and 3745 | 12.2(15)ZJ3 or later
12.2(11)T6 or later 12.3(1)M or later |
| Cisco 3825 and 3845 | 12.3(11)T or later |
| Cisco 7204VXR, 7206VXR, and 7301 | 12.3(2)T or later
12.3(1)M or later No support for B, E, or S train releases on Cisco 7000 routers |
| The information in Table 24-7 is adapted from "Cisco Router and Security Device Manager" at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/products_data_sheet0900aecd800fd118.html.
Cisco SDM is available free of charge on all major Cisco router models from Cisco 830 to Cisco 7301. Cisco SDM ships preinstalled on all new Cisco router 850 Series, 870 Series, 1800 Series, 2800 Series, and the 3800 Series integrated services routers (ISR). | |
As mentioned earlier, Cisco SDM can be launched from any user desktop PC using a supported browser.
Table 24-8 shows the basic list of system requirements for the Cisco SDM application.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Router Flash Memory | Minimum of 6 MB of free Flash memory on the router for Cisco SDM files. Minimum of 2 MB of free Flash memory on the router for Cisco SDM Express. Wireless Management file requires additional 1.7 MB. Rest of the SDM files can be installed on PC hard disk. |
| PC Hardware | Pentium III or later series processor |
| PC Operating System | Windows XP Professional
Windows 2003 Server (Standard Edition) Windows 2000 Professional Windows NT 4.0 Workstation (Service Pack 4) Windows ME Japanese, Simplified Chinese, French, German, Spanish, and Italian language OS support |
| Browser Software | Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5 or later
Netscape Navigator 7.1 and 7.2 Firefox 1.0.5 |
| Java Software | Java Virtual Machine (JVM) built-in browsers required Java plug-in (Java Runtime Environment Version 1.4.2_05 or later) |
| The information in Table 24-8 is taken from "Cisco Router and Security Device Manager" at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/products_data_sheet0900aecd800fd118.html. Windows 2000 (Advanced Server) is not supported by Cisco SDM. | |
For more details to install and configure Cisco SDM, refer to the following Cisco documentations:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/prod_installation_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/products_user_guide_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/prod_configuration_examples_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps5318/prod_technical_reference_list.html