Adaptive Security Algorithm Operation
Figure 6-5 illustrates how the stateful-inspection and application intelligence works in the Security Appliance. Conceptually, three basic operational functions are performed:
Access lists: Controlling network access based on specific networks, hosts, and services (TCP/UDP port numbers).
Connections (xlate and conn tables): Maintaining state information for each connection. This information is used by the Adaptive Security Algorithm and cut-through proxy to effectively forward traffic within established connections.
Inspection Engine: Perform stateful inspection coupled with application-level inspection functions. These inspection rule sets are predefined to validate application compliance as per RFC and other standards and cannot be altered.
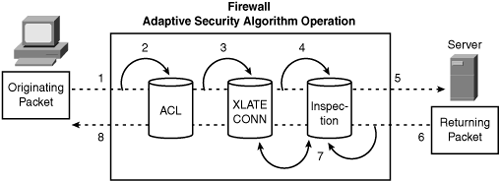
Figure 6-5 is numbered with the operations in the order they occur and are detailed as follows:
An incoming TCP SYN packet arrives on the Security Appliance to establish a new connection.
The Security Appliance checks the access list database to determine whether the connection is permitted.
The Security Appliance creates a new entry in the connection database (XLATE and CONN tables) using the necessary session information.
The Security Appliance checks the predefined rule sets in the inspection engine and in case of well-known applications, further performs application-level inspection.
At this point, Security Appliance makes a decision whether to forward or drop the packet according to the findings of the inspection engine. The Security Appliance forwards the packet to the desired destination subject to clearance from the application inspection engine.
The destination system responds to the initial request returning the packet.
The Security Appliance receives the reply packet, performs the inspection, and looks up the connection in the connection database to determine whether the session information matches an existing connection.
The Security Appliance forwards the packet belonging to an existing established session.
Table 6-2 lists all the application protocols and details for which the Security Appliance provides application layer inspection capability.
